
Subscribe to stay ahead with expert insights on ESOPs, smart ownership strategies, and more!
Editor's Note:- For Indian startups and private limited enterprises wishing to provide Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs), this article offers a systematic legal checklist. In addition to outlining compliance with tax regulations and highlighting best practices for communicating and sustaining ESOP plans, it describes the legal obligations under the Companies Act of 2013. The goal of the handbook is to assist HR directors and founders in successfully implementing ESOPs while maintaining complete compliance.
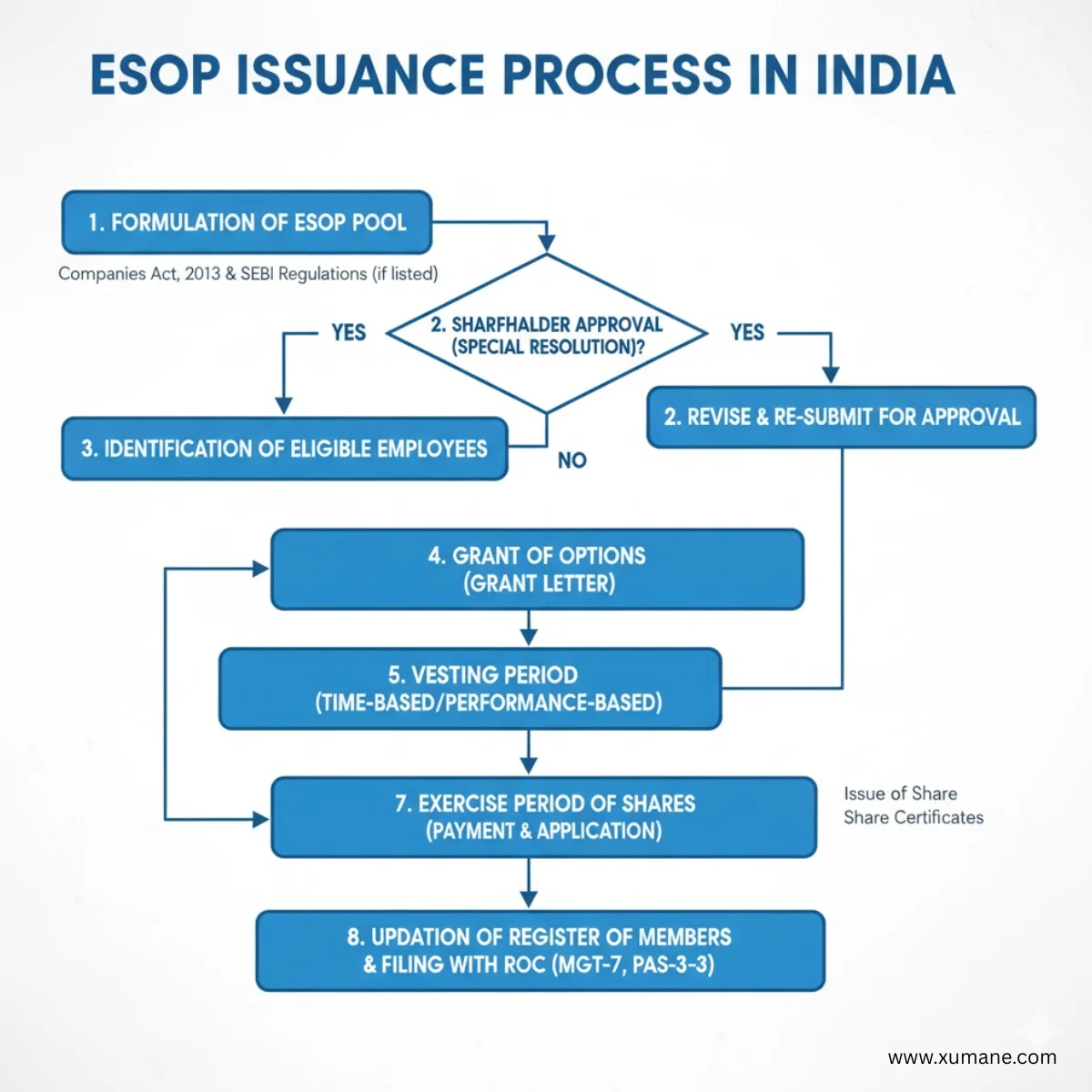
In India, issuing Employee Stock Option Plans (ESOPs) is a calculated step taken by startups and private limited enterprises looking to draw in, keep, and inspire talent. The Companies Act of 2013 and other relevant laws govern this legal procedure, which extends beyond simply creating a plan. Infractions may result in fines, court cases, and difficulties in raising or selling money.
This article offers a thorough legal checklist to make sure your ESOP issuance complies with best practices and Indian corporate rules.
Drafting a thorough ESOP scheme that includes the following details is the first stage.
This plan must adhere to Rule 12 of the Companies (Share Capital and Debentures) Rules, 2014, and it forms the basis for board and shareholder approvals.
If the issuing of ESOPs is not currently permitted by your company's articles of association, this clause needs to be added. To make sure the business has the legal authority to offer its employees options, this step is essential.
Call a board meeting and give at least seven days' notice to:
To get shareholder approval for the ESOP plan, an EGM must be held. All shareholders shall receive notification of the EGM at least 21 days in advance, along with an explanation that includes the following:
A special resolution must be passed by the shareholders to approve the scheme.
Within 30 days of receiving shareholder approval, submit the special resolution in Form MGT-14 to the RoC. In order to comply with the requirements of the Companies Act of 2013, this filing is required.
The business may provide options to qualified workers after obtaining all necessary permissions. Employees should be made aware of the terms and conditions of their alternatives, and the grant should be documented.
Keep a record of the employees who have been given options, including the quantity of options, the vesting timeline, and other relevant details. When necessary, this register should be made available for review and updated on a regular basis.
Make sure that ESOPs are taxed in accordance with the Income Tax Act of 1961. Two phases give rise to tax implications :
Make sure that employees understand the ESOPs' terms and conditions. Give them all the information they require, such as the vesting period, exercise cost, and option exercise procedure. To guarantee employee comprehension and happiness, transparency is essential.
To guarantee continued adherence to relevant rules and regulations, examine and update the ESOP scheme regularly. Keep all required documentation for auditing purposes and notify the RoC of any modifications as needed.
For Indian startups and private limited firms, issuing ESOPs is a potent instrument for coordinating employee interests with business expansion. To guarantee compliance and steer clear of any hazards, it is necessary to thoroughly traverse the legal terrain. Businesses can create a strong and legally sound ESOP framework that benefits the company and its employees by using this checklist.